Description
Origins of Ketamine
Ketamine was first discovered and synthesized in 1962 by Calvin L. Stevens, who was working for Parke-Davis, a pharmaceutical company in the United States at the time. Initially, ketamine was developed as an anesthetic agent due to its ability to induce a state of dissociation, which numbs pain without causing unconsciousness. The drug was quickly approved for use in human medicine, and was widely used as a surgical anesthesia in the 1970s.
Brief History of ketamine
Although originally developed as an anesthetic, ketamine quickly gained popularity in recreational circles due to its ability to produce a hallucinogenic state of consciousness. By the 1990s, ketamine had become a popular street drug, especially in underground rave scenes. The drug’s dissociative effects, which can produce feelings of euphoria and detachment, made it particularly attractive to individuals seeking a mind-altering experience. Today, ketamine is still used as an anesthetic in medical settings, but is still very popular with recreational users.
Forms of Ketamine
There are many forms of Ketamine but the most common kind used for recreational use are below. Effects vary depending on which you take, see the effects sub-section below for more information.
📌 Racemic Ketamine
This is the most common type of ketamine and is a mixture of two different isomers, or chemical compounds. This type of ketamine is typically used in medical settings as an anesthetic.
📌 S-ketamine
This isomer of ketamine is used in nasal spray form for the treatment of severe depression that has not responded to other treatments. It has been shown to have rapid antidepressant effects but is not yet approved for widespread use.
Appearance
Ketamine sold recreationally is often found in shard form or a glassy sand-like texture. This can be cause irritation to the nasal passages if you are snorting the drug. Breaking/crushing the drug down as much as possible is the best way to counteract this.
Positive Effects
Effects are subjective but racemic is said to have more effect on the body whilst S-ketamine tends to have more psychedelic properties. That said, many people tend to prefer the latter.
Both types can cause users to feel:
📌 Like they’re in a dream-like sense of detachment (dissociatiated).
📌 Happy.
📌 Relaced and chilled.
📌 To feel like they are tripping and cause confusion.
📌 It can also very effectively stop pain.
Negative Effects
Negative effects can be:
📌 Nausea.
📌 Depression.
📌 Make you numb to pain to the extent that you may injure yourself unknowingly.
Regular users can develop symptoms such as:
📌 Becoming agitated.
📌 Panic attacks.
📌 Damage to long and short-term memory.
📌 Bladder and liver problems can also emerge with frequent and/or heavy use.
📌 It is believed that ketamine use can exacerbate pre-existing mental health problems.
Addiction
Although not physically addictive, people do become psychologically addicted and tolerance build up can cause users to take increasing amounts.
If you or someone you care about is struggling with addiction, please visit the UKP Addiction Page, and check our some of the links in the Web Resources section towards the end of this page.
Routes of Administration
Ketamine can be consumed through several routes for recreational purposes, including:
📌 Intranasal
Ketamine powder can be snorted through the nose for a fast-acting, intense high. Intranasal use is one of the most common methods of recreational ketamine use.
📌 Injection
Ketamine can be injected directly into a vein for an even more immediate and powerful high. However, injecting ketamine carries a higher risk of addiction and overdose.
📌 Oral
Ketamine can also be consumed orally in the form of pills, capsules, or mixed with food or drink. This method is less common due to the longer onset and weaker effects.
📌 Sublingual
This method involves placing a ketamine lozenge under the tongue where it dissolves and is absorbed through the mucous membranes. Sublingual ketamine has a slower onset than intranasal use but can still produce strong effects.
📌 Rectal
Ketamine can also be administered rectally, which provides rapid absorption while avoiding the negative effects on the nasal mucosa associated with intranasal use. However, this method is not common due to the stigma surrounding the route of administration.
Dosaging
Insufflated
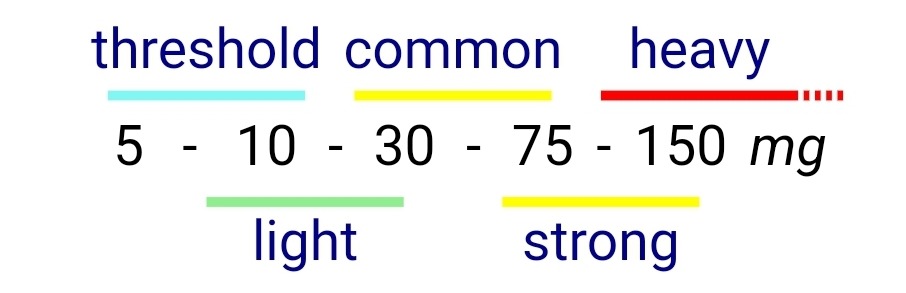
Taken Orally
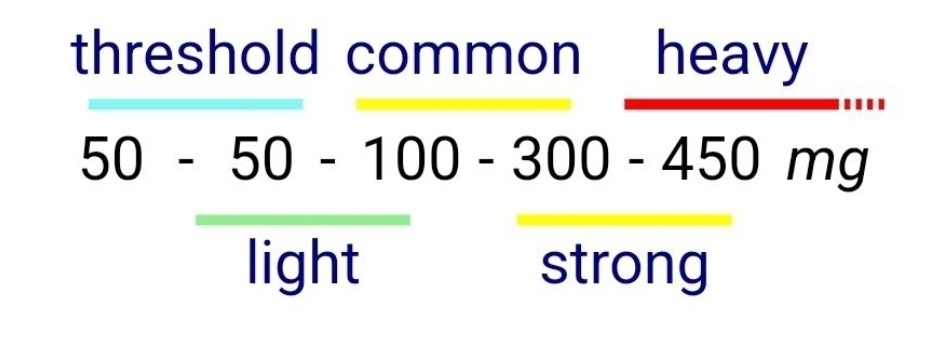
Onset Time and Duration
Insufflated
Users can expect onset within 10 minutes, a come-up time of up to 20 minutes. Effects should peak anywhere between 15-45 minutes and total duration up to an hour, after effects reported to be felt up for up to 12 hours.
Taken Orally
Orally users can expect an onset between 10-30 minutes, a come-up of between 5-20 minutes after this. Effects peak between 45-90 minutes and a total duration of effects up to 6 hours. After effects can last up to 8 hours.
Potential Risky Interactions
Although Ketamine has a relatively good safety profile compared to other recreational drugs, there are always some risks when mixing compounds. These may not be common occurances but are risks.
📌 Alcohol
Combining ketamine with alcohol can increase the risk of side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and difficulty breathing. It can also increase the risk of overdose and lead to dangerous respiratory depression.
📌 Opioids
Combining ketamine with opioids can increase the risk of respiratory depression, coma, and death. These drugs both depress the central nervous system, which can cause dangerous interactions when taken together.
📌 Benzodiazepines
Combining ketamine with benzodiazepines can increase the risk of sedation and respiratory depression. Both of these drugs can cause drowsiness and impaired coordination, which can be dangerous when combined.
📌 Antidepressants
Combining ketamine with certain types of antidepressants such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) can lead to dangerous interactions such as high blood pressure, seizures, and serotonin syndrome.
Detection Times
Detection times are subjective and the below are guidelines only. The best way to pass a drug test is to not take drugs.
📌 Saliva
Ketamine can typically be detected in urine for up to 24 hours.
📌 Urine
General consensus is that Ketamine can be detected in urine up to 14 days after last use. However some studies suggest that it could be detected up to 30 days after last use.
📌 Blood
Ketamine can show up in the blood for up to 3 days, but is more detectable in the first 24 hours after last use.
📌 Hair
If you’re required to undergo hair drub testing just shave your head. It is claimed that Ketamine is detectable for up to 4 months after last use in the hair.
Further Safety Tips
We always encourage basic safety precautions and health maintenance before and during drug use, should you decide to use them. Here are some basic tips:
📌 Test your drugs where possible, especially if you’re buying from an unknown source.
📌 A lot of people use benzodiazepines or other pharmaceutical sleeping tablets to kill a comedown. We urge extreme caution when doing this (especially if you’ve had alcohol too) and recommend trying more natural sleep aids such as melatonin to see if they work for you.
📌 Always start with a low dose and work your way up slowly to avoid the risk of adverse effects. The effects of some substances can be unpredictable, and individual sensitivity can vary greatly.
📌 Use in a safe and comfortable environment: Use substances in a safe and comfortable environment, preferably with someone you trust who can assist you if necessary. Avoid crowded or unfamiliar places that could cause anxiety or distress.
📌 Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, but be careful not to drink too much as this can lead to hyponatremia (low sodium levels in the blood), which can be life-threatening.
📌 Be careful when combining with other drugs. Research what drugs interact with each other an risk adverse effects.
📌 Take breaks between uses. As a general rule limit your use to 1-2 times per week.
📌 Seek medical attention if necessary. Your health is an absolute priority and not worth risk because you fear somebody finding out about your drug use.
📌 We recommend that you take a multi-vitamin the morning after or with food and take liver function tablets the morning of the day of drug use and again the morning after. Drink plenty of water before bed after use. If you take drugs every week then take liver function tablets every day. However, we recommend that if you choose to use drugs, then try to limit use to 1-2 times per week maximum.
buy ketamine uk,buy ketamine uk,buy ketamine uk,buy ketamine uk,buy ketamine uk















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.